[Flutter] 기본위젯
- 자식을 하나만 갖는 위젯
| 자식을 하나만 갖는 대표적인 위젯 대체로 child 매개변수 입력 받는 항목 |
| Container : - 자식을 담는 컨테이너 역할. - 배경색 , 너비와 높이, 테두리 등의 디자인 지정가능 |
| GestureDetecotr 위젯 : - 플러터에서 제공하는 제스처 기능을 자식 위젯에서 인식하는 위젯 - 탭이나 드래그 그리고 더블 클릭 같은 제스처 기능이 자식 위젯에 인식 됐을때 함수를 실행 |
| SizeBox 위젯 : - 높이와 너비를 지정하는 위젯 - Container 위젯과 다르게 디자인적 요소는 적용할 수 없고 Const 생성자로 선언할 수 있어서 퍼포먼스 측면에서 효율적 |
- 자식을 여러개 갖는 위젯
| 다수의 자식을 입력 받는 위젯의 경우에는 children 매개변수를 입력 가능, 리스트로 여러 위젯 입력가능 |
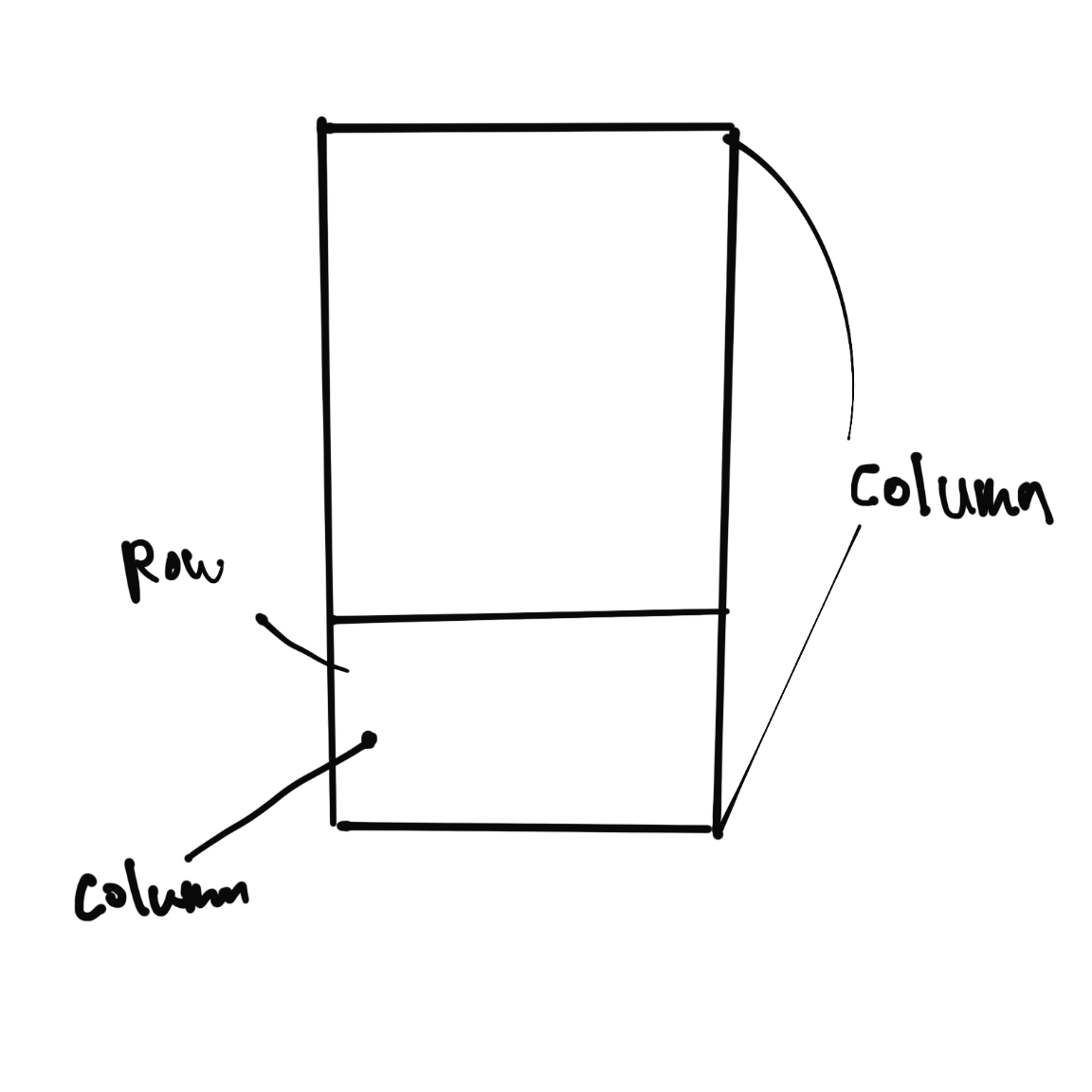
| Column 위젯 : - children 매개변수에 입력된 모든 위젯들을 세로로 배치한다. |
| Row 위젯 : - children 매개변수에 입력된 모든 위젯들을 가로로 배치한다. |
| ListView : - 리스트를 구현할 때 사용 - children 매개변수에 다수의 위젯을 입력 가능 - 입력된 위젯이 화면을 벗어나면 스크롤 가능해진다. |
- Children 와 Child의 차이점
| 공통점 : child 매개변수와 children 매개변수는 위젯에 하위 위젯을 추가할 때 사용 |
| 차이점 : child 매개변수는 한개 , children 매개변수는 여러개 입력가능 |
| 기타사항 : child 와 children 매개변수를 동시에 입력받는 위젯은 존재하지 않는다. |
- 소스코드부분 ( 텍스트 관련 위젯 입력)
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() {
runApp(const MyApp());
}
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
const MyApp({super.key});
// This widget is the root of your application.
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
home: Scaffold(
body:Center(
child:Text('코드입력',
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 16.0,
fontWeight: FontWeight.w700,
color: Colors.blue,
),
)
),
),
);
}
}
class MyHomePage extends StatefulWidget {
const MyHomePage({super.key, required this.title});
// This widget is the home page of your application. It is stateful, meaning
// that it has a State object (defined below) that contains fields that affect
// how it looks.
// This class is the configuration for the state. It holds the values (in this
// case the title) provided by the parent (in this case the App widget) and
// used by the build method of the State. Fields in a Widget subclass are
// always marked "final".
final String title;
@override
State<MyHomePage> createState() => _MyHomePageState();
}
class _MyHomePageState extends State<MyHomePage> {
int _counter = 0;
void _incrementCounter() {
setState(() {
// This call to setState tells the Flutter framework that something has
// changed in this State, which causes it to rerun the build method below
// so that the display can reflect the updated values. If we changed
// _counter without calling setState(), then the build method would not be
// called again, and so nothing would appear to happen.
_counter++;
});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
// This method is rerun every time setState is called, for instance as done
// by the _incrementCounter method above.
//
// The Flutter framework has been optimized to make rerunning build methods
// fast, so that you can just rebuild anything that needs updating rather
// than having to individually change instances of widgets.
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
// Here we take the value from the MyHomePage object that was created by
// the App.build method, and use it to set our appbar title.
title: Text(widget.title),
),
body: Center(
// Center is a layout widget. It takes a single child and positions it
// in the middle of the parent.
child: Column(
// Column is also a layout widget. It takes a list of children and
// arranges them vertically. By default, it sizes itself to fit its
// children horizontally, and tries to be as tall as its parent.
//
// Invoke "debug painting" (press "p" in the console, choose the
// "Toggle Debug Paint" action from the Flutter Inspector in Android
// Studio, or the "Toggle Debug Paint" command in Visual Studio Code)
// to see the wireframe for each widget.
//
// Column has various properties to control how it sizes itself and
// how it positions its children. Here we use mainAxisAlignment to
// center the children vertically; the main axis here is the vertical
// axis because Columns are vertical (the cross axis would be
// horizontal).
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: <Widget>[
const Text(
'You have pushed the button this many times:',
),
Text(
'$_counter',
style: Theme.of(context).textTheme.headlineMedium,
),
],
),
),
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
onPressed: _incrementCounter,
tooltip: 'Increment',
child: const Icon(Icons.add),
), // This trailing comma makes auto-formatting nicer for build methods.
);
}
}
- 제스처 관련 위젯 : 사용자가 키보드로 글자를 입력하는 행위 외에 모든 입력을 제스처 라고 지칭함
- ex) 두번 탭 / 길게 버튼을 누르는 행위 /등등
- 텍스트형 버튼소스
- 소스코드
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() {
runApp(const MyApp());
}
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
const MyApp({super.key});
// This widget is the root of your application.
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
home: Scaffold(
body:Center(
child: TextButton(
//클릭시 실행
onPressed: (){},
//스타일 지정
style: TextButton.styleFrom(
//주 색상지정
foregroundColor: Colors.red,
),
//버튼에 넣을 위젯
child: Text('텍스트형 버튼'),
)
),
),
);
}
}
class MyHomePage extends StatefulWidget {
const MyHomePage({super.key, required this.title});
// This widget is the home page of your application. It is stateful, meaning
// that it has a State object (defined below) that contains fields that affect
// how it looks.
// This class is the configuration for the state. It holds the values (in this
// case the title) provided by the parent (in this case the App widget) and
// used by the build method of the State. Fields in a Widget subclass are
// always marked "final".
final String title;
@override
State<MyHomePage> createState() => _MyHomePageState();
}
class _MyHomePageState extends State<MyHomePage> {
int _counter = 0;
void _incrementCounter() {
setState(() {
// This call to setState tells the Flutter framework that something has
// changed in this State, which causes it to rerun the build method below
// so that the display can reflect the updated values. If we changed
// _counter without calling setState(), then the build method would not be
// called again, and so nothing would appear to happen.
_counter++;
});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
// This method is rerun every time setState is called, for instance as done
// by the _incrementCounter method above.
//
// The Flutter framework has been optimized to make rerunning build methods
// fast, so that you can just rebuild anything that needs updating rather
// than having to individually change instances of widgets.
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
// Here we take the value from the MyHomePage object that was created by
// the App.build method, and use it to set our appbar title.
title: Text(widget.title),
),
body: Center(
// Center is a layout widget. It takes a single child and positions it
// in the middle of the parent.
child: Column(
// Column is also a layout widget. It takes a list of children and
// arranges them vertically. By default, it sizes itself to fit its
// children horizontally, and tries to be as tall as its parent.
//
// Invoke "debug painting" (press "p" in the console, choose the
// "Toggle Debug Paint" action from the Flutter Inspector in Android
// Studio, or the "Toggle Debug Paint" command in Visual Studio Code)
// to see the wireframe for each widget.
//
// Column has various properties to control how it sizes itself and
// how it positions its children. Here we use mainAxisAlignment to
// center the children vertically; the main axis here is the vertical
// axis because Columns are vertical (the cross axis would be
// horizontal).
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: <Widget>[
const Text(
'You have pushed the button this many times:',
),
Text(
'$_counter',
style: Theme.of(context).textTheme.headlineMedium,
),
],
),
),
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
onPressed: _incrementCounter,
tooltip: 'Increment',
child: const Icon(Icons.add),
), // This trailing comma makes auto-formatting nicer for build methods.
);
}
}
- 아웃라인드버튼 - 테투리가 있는 버튼 소스
- 소스코드
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() {
runApp(const MyApp());
}
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
const MyApp({super.key});
// This widget is the root of your application.
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
home: Scaffold(
body:Center(
// child: TextButton(
// //클릭시 실행
// onPressed: (){},
// //스타일 지정
// style: TextButton.styleFrom(
// //주 색상지정
// foregroundColor: Colors.red,
// ),
// //버튼에 넣을 위젯
// child: Text('텍스트형 버튼'),
// )
child: OutlinedButton(
//클릭시 실행할 함수
onPressed: (){},
//버튼 스타일
style: OutlinedButton.styleFrom(
foregroundColor: Colors.red,
),
//버튼에 들어갈 위젯
child: Text('아웃라인드 버튼'),
),
),
),
);
}
}
class MyHomePage extends StatefulWidget {
const MyHomePage({super.key, required this.title});
// This widget is the home page of your application. It is stateful, meaning
// that it has a State object (defined below) that contains fields that affect
// how it looks.
// This class is the configuration for the state. It holds the values (in this
// case the title) provided by the parent (in this case the App widget) and
// used by the build method of the State. Fields in a Widget subclass are
// always marked "final".
final String title;
@override
State<MyHomePage> createState() => _MyHomePageState();
}
class _MyHomePageState extends State<MyHomePage> {
int _counter = 0;
void _incrementCounter() {
setState(() {
// This call to setState tells the Flutter framework that something has
// changed in this State, which causes it to rerun the build method below
// so that the display can reflect the updated values. If we changed
// _counter without calling setState(), then the build method would not be
// called again, and so nothing would appear to happen.
_counter++;
});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
// This method is rerun every time setState is called, for instance as done
// by the _incrementCounter method above.
//
// The Flutter framework has been optimized to make rerunning build methods
// fast, so that you can just rebuild anything that needs updating rather
// than having to individually change instances of widgets.
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
// Here we take the value from the MyHomePage object that was created by
// the App.build method, and use it to set our appbar title.
title: Text(widget.title),
),
body: Center(
// Center is a layout widget. It takes a single child and positions it
// in the middle of the parent.
child: Column(
// Column is also a layout widget. It takes a list of children and
// arranges them vertically. By default, it sizes itself to fit its
// children horizontally, and tries to be as tall as its parent.
//
// Invoke "debug painting" (press "p" in the console, choose the
// "Toggle Debug Paint" action from the Flutter Inspector in Android
// Studio, or the "Toggle Debug Paint" command in Visual Studio Code)
// to see the wireframe for each widget.
//
// Column has various properties to control how it sizes itself and
// how it positions its children. Here we use mainAxisAlignment to
// center the children vertically; the main axis here is the vertical
// axis because Columns are vertical (the cross axis would be
// horizontal).
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: <Widget>[
const Text(
'You have pushed the button this many times:',
),
Text(
'$_counter',
style: Theme.of(context).textTheme.headlineMedium,
),
],
),
),
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
onPressed: _incrementCounter,
tooltip: 'Increment',
child: const Icon(Icons.add),
), // This trailing comma makes auto-formatting nicer for build methods.
);
}
}
- ElevatedButton - 입체적으로 튀어나온 형태의 버튼 형태 소스 코드
- 소스코드
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() {
runApp(const MyApp());
}
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
const MyApp({super.key});
// This widget is the root of your application.
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
home: Scaffold(
body:Center(
// child: TextButton(
// //클릭시 실행
// onPressed: (){},
// //스타일 지정
// style: TextButton.styleFrom(
// //주 색상지정
// foregroundColor: Colors.red,
// ),
// //버튼에 넣을 위젯
// child: Text('텍스트형 버튼'),
// )
// child: OutlinedButton(
// //클릭시 실행할 함수
// onPressed: (){},
// //버튼 스타일
// style: OutlinedButton.styleFrom(
// foregroundColor: Colors.red,
// ),
// //버튼에 들어갈 위젯
// child: Text('아웃라인드 버튼'),
// ),
child: ElevatedButton(
//클릭시 실행할 함수
onPressed: (){},
//버튼 스타일
style: ElevatedButton.styleFrom(
backgroundColor: Colors.red,
),
//버튼에 들어갈 위젯
child: Text('입체적버튼 버튼'),
),
),
),
);
}
}
class MyHomePage extends StatefulWidget {
const MyHomePage({super.key, required this.title});
// This widget is the home page of your application. It is stateful, meaning
// that it has a State object (defined below) that contains fields that affect
// how it looks.
// This class is the configuration for the state. It holds the values (in this
// case the title) provided by the parent (in this case the App widget) and
// used by the build method of the State. Fields in a Widget subclass are
// always marked "final".
final String title;
@override
State<MyHomePage> createState() => _MyHomePageState();
}
class _MyHomePageState extends State<MyHomePage> {
int _counter = 0;
void _incrementCounter() {
setState(() {
// This call to setState tells the Flutter framework that something has
// changed in this State, which causes it to rerun the build method below
// so that the display can reflect the updated values. If we changed
// _counter without calling setState(), then the build method would not be
// called again, and so nothing would appear to happen.
_counter++;
});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
// This method is rerun every time setState is called, for instance as done
// by the _incrementCounter method above.
//
// The Flutter framework has been optimized to make rerunning build methods
// fast, so that you can just rebuild anything that needs updating rather
// than having to individually change instances of widgets.
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
// Here we take the value from the MyHomePage object that was created by
// the App.build method, and use it to set our appbar title.
title: Text(widget.title),
),
body: Center(
// Center is a layout widget. It takes a single child and positions it
// in the middle of the parent.
child: Column(
// Column is also a layout widget. It takes a list of children and
// arranges them vertically. By default, it sizes itself to fit its
// children horizontally, and tries to be as tall as its parent.
//
// Invoke "debug painting" (press "p" in the console, choose the
// "Toggle Debug Paint" action from the Flutter Inspector in Android
// Studio, or the "Toggle Debug Paint" command in Visual Studio Code)
// to see the wireframe for each widget.
//
// Column has various properties to control how it sizes itself and
// how it positions its children. Here we use mainAxisAlignment to
// center the children vertically; the main axis here is the vertical
// axis because Columns are vertical (the cross axis would be
// horizontal).
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: <Widget>[
const Text(
'You have pushed the button this many times:',
),
Text(
'$_counter',
style: Theme.of(context).textTheme.headlineMedium,
),
],
),
),
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
onPressed: _incrementCounter,
tooltip: 'Increment',
child: const Icon(Icons.add),
), // This trailing comma makes auto-formatting nicer for build methods.
);
}
}- 아이콘이 있는 버튼
- 소스코드
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() {
runApp(const MyApp());
}
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
const MyApp({super.key});
// This widget is the root of your application.
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
home: Scaffold(
body:Center(
// child: TextButton(
// //클릭시 실행
// onPressed: (){},
// //스타일 지정
// style: TextButton.styleFrom(
// //주 색상지정
// foregroundColor: Colors.red,
// ),
// //버튼에 넣을 위젯
// child: Text('텍스트형 버튼'),
// )
// child: OutlinedButton(
// //클릭시 실행할 함수
// onPressed: (){},
// //버튼 스타일
// style: OutlinedButton.styleFrom(
// foregroundColor: Colors.red,
// ),
// //버튼에 들어갈 위젯
// child: Text('아웃라인드 버튼'),
// ),
// child: ElevatedButton(
// //클릭시 실행할 함수
// onPressed: (){},
// //버튼 스타일
// style: ElevatedButton.styleFrom(
// backgroundColor: Colors.red,
// ),
// //버튼에 들어갈 위젯
// child: Text('입체적버튼 버튼'),
// ),
child: IconButton(
onPressed: (){},
icon:Icon(
//플러터에서 기본저긍로 제공하는 아이콘
//링크 확인 --> https://fonts.google.com/icons
Icons.home,
)
),
),
),
);
}
}
class MyHomePage extends StatefulWidget {
const MyHomePage({super.key, required this.title});
// This widget is the home page of your application. It is stateful, meaning
// that it has a State object (defined below) that contains fields that affect
// how it looks.
// This class is the configuration for the state. It holds the values (in this
// case the title) provided by the parent (in this case the App widget) and
// used by the build method of the State. Fields in a Widget subclass are
// always marked "final".
final String title;
@override
State<MyHomePage> createState() => _MyHomePageState();
}
class _MyHomePageState extends State<MyHomePage> {
int _counter = 0;
void _incrementCounter() {
setState(() {
// This call to setState tells the Flutter framework that something has
// changed in this State, which causes it to rerun the build method below
// so that the display can reflect the updated values. If we changed
// _counter without calling setState(), then the build method would not be
// called again, and so nothing would appear to happen.
_counter++;
});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
// This method is rerun every time setState is called, for instance as done
// by the _incrementCounter method above.
//
// The Flutter framework has been optimized to make rerunning build methods
// fast, so that you can just rebuild anything that needs updating rather
// than having to individually change instances of widgets.
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
// Here we take the value from the MyHomePage object that was created by
// the App.build method, and use it to set our appbar title.
title: Text(widget.title),
),
body: Center(
// Center is a layout widget. It takes a single child and positions it
// in the middle of the parent.
child: Column(
// Column is also a layout widget. It takes a list of children and
// arranges them vertically. By default, it sizes itself to fit its
// children horizontally, and tries to be as tall as its parent.
//
// Invoke "debug painting" (press "p" in the console, choose the
// "Toggle Debug Paint" action from the Flutter Inspector in Android
// Studio, or the "Toggle Debug Paint" command in Visual Studio Code)
// to see the wireframe for each widget.
//
// Column has various properties to control how it sizes itself and
// how it positions its children. Here we use mainAxisAlignment to
// center the children vertically; the main axis here is the vertical
// axis because Columns are vertical (the cross axis would be
// horizontal).
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: <Widget>[
const Text(
'You have pushed the button this many times:',
),
Text(
'$_counter',
style: Theme.of(context).textTheme.headlineMedium,
),
],
),
),
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
onPressed: _incrementCounter,
tooltip: 'Increment',
child: const Icon(Icons.add),
), // This trailing comma makes auto-formatting nicer for build methods.
);
}
}
- GestureDetcor 위젯 : 사용자가 손가락하는 여러 가지 입력을 인지하는 위젯
- 소스코드
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() {
runApp(const MyApp());
}
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
const MyApp({super.key});
// This widget is the root of your application.
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
home: Scaffold(
body:Center(
child:GestureDetector(
// 한 번 탭 했을때 실행할 함수
onTap: (){
// 출력 결과는 안드로이드 스튜디오의 런 탭에서 확인 가능합니다
print('on tap');
},
// 두번 탭 했을 때 실행할 함수
onDoubleTap: (){
print('on double tap');
},
//3 길게 눌렀을때 실행할 함수
onLongPress: (){
print('on long press');
},
//제스처를 적용할 위젯
child: Container(
decoration: BoxDecoration(
color: Colors.red,
),
width: 100.0,
height: 100.0,
),
),
),
),
);
}
}
class MyHomePage extends StatefulWidget {
const MyHomePage({super.key, required this.title});
// This widget is the home page of your application. It is stateful, meaning
// that it has a State object (defined below) that contains fields that affect
// how it looks.
// This class is the configuration for the state. It holds the values (in this
// case the title) provided by the parent (in this case the App widget) and
// used by the build method of the State. Fields in a Widget subclass are
// always marked "final".
final String title;
@override
State<MyHomePage> createState() => _MyHomePageState();
}
class _MyHomePageState extends State<MyHomePage> {
int _counter = 0;
void _incrementCounter() {
setState(() {
// This call to setState tells the Flutter framework that something has
// changed in this State, which causes it to rerun the build method below
// so that the display can reflect the updated values. If we changed
// _counter without calling setState(), then the build method would not be
// called again, and so nothing would appear to happen.
_counter++;
});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
// This method is rerun every time setState is called, for instance as done
// by the _incrementCounter method above.
//
// The Flutter framework has been optimized to make rerunning build methods
// fast, so that you can just rebuild anything that needs updating rather
// than having to individually change instances of widgets.
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
// Here we take the value from the MyHomePage object that was created by
// the App.build method, and use it to set our appbar title.
title: Text(widget.title),
),
body: Center(
// Center is a layout widget. It takes a single child and positions it
// in the middle of the parent.
child: Column(
// Column is also a layout widget. It takes a list of children and
// arranges them vertically. By default, it sizes itself to fit its
// children horizontally, and tries to be as tall as its parent.
//
// Invoke "debug painting" (press "p" in the console, choose the
// "Toggle Debug Paint" action from the Flutter Inspector in Android
// Studio, or the "Toggle Debug Paint" command in Visual Studio Code)
// to see the wireframe for each widget.
//
// Column has various properties to control how it sizes itself and
// how it positions its children. Here we use mainAxisAlignment to
// center the children vertically; the main axis here is the vertical
// axis because Columns are vertical (the cross axis would be
// horizontal).
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: <Widget>[
const Text(
'You have pushed the button this many times:',
),
Text(
'$_counter',
style: Theme.of(context).textTheme.headlineMedium,
),
],
),
),
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
onPressed: _incrementCounter,
tooltip: 'Increment',
child: const Icon(Icons.add),
), // This trailing comma makes auto-formatting nicer for build methods.
);
}
}
GestureDetector 위젯에서 제공하는 제스처 매개변수
| 매개변수 | 설명 |
| onTap | 한 번 탭했을때 실행되는 함수를 입력할 수 있습니다. |
| onDoubleTap | 두 번 연속으로 탭했을때 실행되는 함수를 입력할 수 있습니다. |
| onLongPress | 길게 누르기가 인색됐을 때 실행되는 함수를 입력 할 수 있습니다. |
| onPanStart | 수평 또는 수직으로 드래그가 시작됐을때 실행되는 함수를 입력 할 수 있습니다. |
| onPanUpdate | 수평 또는 수직으로 드래그를 하는 동안 드래그 위치가 업데이트될 때마다 실행되는 함수를 입력할 수 있습니다. |
| onPanEnd | 수평 또는 수직으로 드래그가 끝났을 때 실행되는 함수를 입력할 수 있습니다. |
| onHorizontalDragStart | 수평으로 드래그를 시작햇을때 실행되는 함수를 입력 할 수 있습니다. |
| onHorizontalDragUpdate | 수평으로 드래그를 하는동안 드래그 위치가 업데이트 될때마다 실행되는 함수 입력가능 |
- 플로팅 버튼
- 소스코드
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() {
runApp(const MyApp());
}
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
const MyApp({super.key});
// This widget is the root of your application.
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
home: Scaffold(
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
//클릭햇을때 실행할 함수
onPressed: (){},
child: Text('클릭'),
),
body: Container(),
),
);
}
}
class MyHomePage extends StatefulWidget {
const MyHomePage({super.key, required this.title});
// This widget is the home page of your application. It is stateful, meaning
// that it has a State object (defined below) that contains fields that affect
// how it looks.
// This class is the configuration for the state. It holds the values (in this
// case the title) provided by the parent (in this case the App widget) and
// used by the build method of the State. Fields in a Widget subclass are
// always marked "final".
final String title;
@override
State<MyHomePage> createState() => _MyHomePageState();
}
class _MyHomePageState extends State<MyHomePage> {
int _counter = 0;
void _incrementCounter() {
setState(() {
// This call to setState tells the Flutter framework that something has
// changed in this State, which causes it to rerun the build method below
// so that the display can reflect the updated values. If we changed
// _counter without calling setState(), then the build method would not be
// called again, and so nothing would appear to happen.
_counter++;
});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
// This method is rerun every time setState is called, for instance as done
// by the _incrementCounter method above.
//
// The Flutter framework has been optimized to make rerunning build methods
// fast, so that you can just rebuild anything that needs updating rather
// than having to individually change instances of widgets.
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
// Here we take the value from the MyHomePage object that was created by
// the App.build method, and use it to set our appbar title.
title: Text(widget.title),
),
body: Center(
// Center is a layout widget. It takes a single child and positions it
// in the middle of the parent.
child: Column(
// Column is also a layout widget. It takes a list of children and
// arranges them vertically. By default, it sizes itself to fit its
// children horizontally, and tries to be as tall as its parent.
//
// Invoke "debug painting" (press "p" in the console, choose the
// "Toggle Debug Paint" action from the Flutter Inspector in Android
// Studio, or the "Toggle Debug Paint" command in Visual Studio Code)
// to see the wireframe for each widget.
//
// Column has various properties to control how it sizes itself and
// how it positions its children. Here we use mainAxisAlignment to
// center the children vertically; the main axis here is the vertical
// axis because Columns are vertical (the cross axis would be
// horizontal).
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: <Widget>[
const Text(
'You have pushed the button this many times:',
),
Text(
'$_counter',
style: Theme.of(context).textTheme.headlineMedium,
),
],
),
),
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
onPressed: _incrementCounter,
tooltip: 'Increment',
child: const Icon(Icons.add),
), // This trailing comma makes auto-formatting nicer for build methods.
);
}
}
위의 책 내용은 모두 코드팩토리의 플러터프로그래밍 소스코드를 공부하면서 작성된 내용입니다. 강력추천합니다!!!!
반응형
'Flutter' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Flutter]Container, SizedBox 위젯 사용법 (0) | 2023.12.09 |
|---|---|
| [Flutter] Column, Row, Expanded 위젯 (0) | 2023.12.09 |
| [Flutter] 위젯 및 Route 및 단축키 (2) | 2023.11.25 |
| Flutter 기본 문법 (0) | 2023.10.21 |
| [Flutter] 웹뷰 관련 (0) | 2023.06.17 |